Piles (Hemorrhoids): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. They can cause discomfort, pain, itching, and bleeding.
Types of Piles
- Internal Hemorrhoids – Located inside the rectum; usually painless but may cause bleeding.
- External Hemorrhoids – Found under the skin around the anus; can be painful, itchy, and swollen.
- Thrombosed Hemorrhoids – A blood clot forms inside an external hemorrhoid, causing severe pain and swelling.
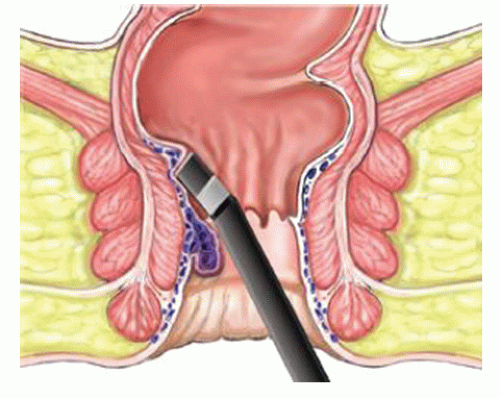
- Prolapsed Hemorrhoids – Internal hemorrhoids that bulge out of the anus and may require medical attention.
Causes
Piles develop due to increased pressure on the veins in the rectal area. Common causes include:
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea – Straining during bowel movements.
- Low-fiber diet – Leads to hard stools.
- Prolonged sitting – Especially on the toilet.
- Pregnancy – Increased pressure in the pelvic region.
- Obesity – Excess weight puts strain on rectal veins.
- Aging – Weakening of rectal tissues over time.
- Heavy lifting – Puts pressure on the abdomen and rectum.
Symptoms
- Pain or discomfort around the anus.
- Itching or irritation in the anal area.
- Bright red bleeding (especially during bowel movements).
- Swelling or lumps near the anus.
- Mucus discharge after passing stool.
- A feeling of incomplete bowel emptying.
Diagnosis
- Physical examination (for external piles).
- Digital rectal exam (doctor inserts a gloved finger to check for internal piles).
- Anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy (a small camera is used to examine internal hemorrhoids).
Treatment
1. Home Remedies & Lifestyle Changes
- High-fiber diet – Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to soften stools.
- Drink plenty of water – Prevents constipation.
- Avoid straining – Do not push too hard while passing stools.
- Warm sitz baths – Soaking in warm water for 15-20 minutes can relieve pain.
- Ice packs – Reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Avoid prolonged sitting – Take breaks and move around.
2. Medications
- Over-the-counter creams & ointments (e.g., hydrocortisone, lidocaine) – Relieve pain and itching.
- Stool softeners – Help with easier bowel movements.
- Pain relievers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen) – Reduce discomfort.
3. Medical Procedures (for severe cases)
- Rubber band ligation – A small band is placed around the hemorrhoid to cut off blood supply.
- Sclerotherapy – A chemical injection shrinks the hemorrhoid.
- Coagulation therapy – Heat or laser treatment to shrink piles.
- Surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy) – Removal of large or persistent hemorrhoids.
Prevention Tips
- Eat more fiber to prevent constipation.
- Stay hydrated to keep stools soft.
- Exercise regularly to improve digestion.
- Avoid prolonged sitting on the toilet.
- Go to the toilet when you feel the urge—don’t delay.
Piles are treatable and preventable with proper care. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a doctor.
Would you like recommendations for home treatments or surgical options? 😊

