Sunburn (Solar Dermatitis): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
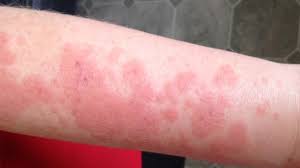
Sunburn, also known as solar dermatitis, is skin damage caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources (like tanning beds). It leads to redness, pain, swelling, and, in severe cases, blisters and peeling.
Causes of Sunburn
- Prolonged UV Exposure: Staying in the sun without protection, especially between 10 AM and 4 PM when UV rays are strongest.
- Lack of Sunscreen: Not applying or using low-SPF sunscreen.
- Fair Skin: Lighter skin tones have less melanin and burn more easily.
- High Altitudes & Reflection: Snow, water, and sand reflect UV rays, increasing exposure.
Symptoms of Sunburn
Mild Sunburn (First-Degree Burn)
- Red, warm, and painful skin.
- Tightness and slight swelling.
- Peeling after a few days.
Severe Sunburn (Second-Degree Burn)
- Blisters filled with fluid.
- Severe pain and deep redness.
- Swelling and skin sensitivity.
- Headache, fever, nausea (signs of sun poisoning).
Treatment for Sunburn
Immediate Relief
Cool the Skin:
- Take a cool (not ice-cold) bath or shower.
- Apply cold compresses for relief.
Moisturize & Hydrate:
- Use aloe vera gel or moisturizer with no alcohol.
- Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration.
Pain Relief:
- Take NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin) to reduce pain and swelling.
- Use hydrocortisone cream for inflammation.
Do Not Pop Blisters:
- If blisters form, let them heal naturally to prevent infection.
Home Remedies for Sunburn
- Aloe Vera: Soothes and hydrates burned skin.
- Coconut Oil: Helps restore moisture but should be applied after initial cooling.
- Oatmeal Bath: Reduces itchiness and irritation.
- Cucumber or Yogurt: Cools and reduces inflammation.
What to Avoid
- Hot showers (can worsen inflammation).
- Harsh soaps and scrubs (irritate skin).
- Tight clothing (prevents skin from healing).
Prevention of Sunburn
- Use Sunscreen: SPF 30+ (apply every 2 hours, or after swimming/sweating).
- Wear Protective Clothing: Hats, sunglasses, and UV-blocking clothes.
- Stay in Shade: Especially during peak sun hours.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Artificial UV exposure also damages the skin.
When to See a Doctor
- Severe blistering over large areas.
- High fever, nausea, dizziness, or chills (sun poisoning).
- Signs of infection (pus, extreme pain, swelling).
Long-Term Effects of Sunburn
- Skin Aging: Wrinkles, dark spots, and loss of elasticity.
- Increased Skin Cancer Risk: UV damage can lead to melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.

