Uterine Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
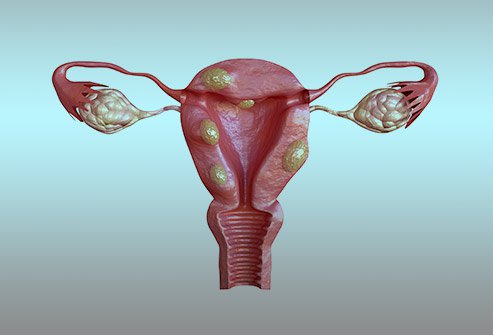
Uterine fibroids (also called leiomyomas or myomas) are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They vary in size, from tiny, undetectable nodules to large masses that can distort the uterus. Fibroids are common in women of reproductive age and may cause symptoms or remain asymptomatic.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
🔹 Hormonal factors – Estrogen & progesterone stimulate fibroid growth.
🔹 Genetic predisposition – Family history increases risk.
🔹 Growth factors – Insulin-like growth factors may influence development.
🔹 Lifestyle factors – Poor diet, obesity, and high stress can contribute.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding (can lead to anemia).
Pelvic pain or pressure.
Frequent urination (if fibroids press on the bladder).
Lower back pain.
Pain during intercourse.
Bloating or abdominal swelling (in large fibroids).
Infertility or pregnancy complications (in some cases).
Diagnosis of Uterine Fibroids
Pelvic exam – Checks for an enlarged uterus.
Ultrasound – Confirms fibroid location & size.
Blood tests – Checks for anemia (due to heavy bleeding).
MRI or CT scan – For detailed imaging of large fibroids.
Hysteroscopy – A thin camera is inserted into the uterus for internal examination.
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
1. Medications
Hormonal therapy – Birth control pills or progesterone IUD to control bleeding.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists – Shrinks fibroids before surgery.
Pain relievers – Ibuprofen or acetaminophen for discomfort.
Iron supplements – For anemia due to heavy bleeding.
2. Non-Surgical Procedures
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) – Blocks blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
MRI-guided focused ultrasound (FUS) – Uses ultrasound waves to break down fibroids.
3. Surgical Options
Myomectomy – Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus (for women who want to conceive).
Hysterectomy – Removes the uterus (only for severe cases or when no pregnancy is planned).
Lifestyle & Home Remedies
Healthy diet – Eat fiber-rich foods (fruits, vegetables, whole grains).
Stay hydrated – Flushes out toxins and supports hormone balance.
Manage stress – Yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Regular exercise – Helps maintain a healthy weight & hormone balance.

