Uveitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
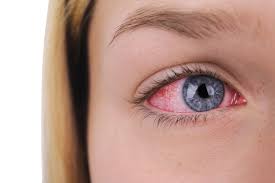
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It can cause eye redness, pain, blurred vision, and light sensitivity. If untreated, it may lead to vision loss.
Causes of Uveitis
🔹 Autoimmune diseases – Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, sarcoidosis.
🔹 Infections – Herpes, syphilis, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis.
🔹 Eye injuries or surgery – Trauma-induced inflammation.
🔹 Certain medications – Antibiotics or bisphosphonates can trigger inflammation.
🔹 Idiopathic (unknown cause) – In many cases, no clear cause is found.
Types of Uveitis & Symptoms
1. Anterior Uveitis (Iritis) – Most Common Type
Eye redness & pain
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Blurred vision
2. Intermediate Uveitis (Cyclitis)
Blurred vision
Floaters (spots or shadows in vision)
Mild eye pain
3. Posterior Uveitis (Choroiditis & Retinitis)
Vision loss or blurriness
Floaters
Usually painless
4. Panuveitis (All Layers Affected – Most Severe)
A combination of all symptoms above
Risk of permanent vision loss
Diagnosis of Uveitis
Eye exam – Checking for inflammation in different parts of the eye.
Blood tests – To rule out infections or autoimmune diseases.
OCT scan or Fundoscopy – Detailed imaging of the retina.
Fluorescein angiography – To examine blood vessels in the eye.
Surgical Options (For Severe Cases)
Vitrectomy – Removal of the vitreous gel to treat complications.
Steroid implants – Long-term treatment for chronic uveitis.
Lifestyle & Home Care
Wear sunglasses – To reduce light sensitivity.
Stay hydrated – Helps maintain eye health.
Avoid smoking & alcohol – Can worsen inflammation.
Manage stress – Meditation & relaxation techniques may help.

