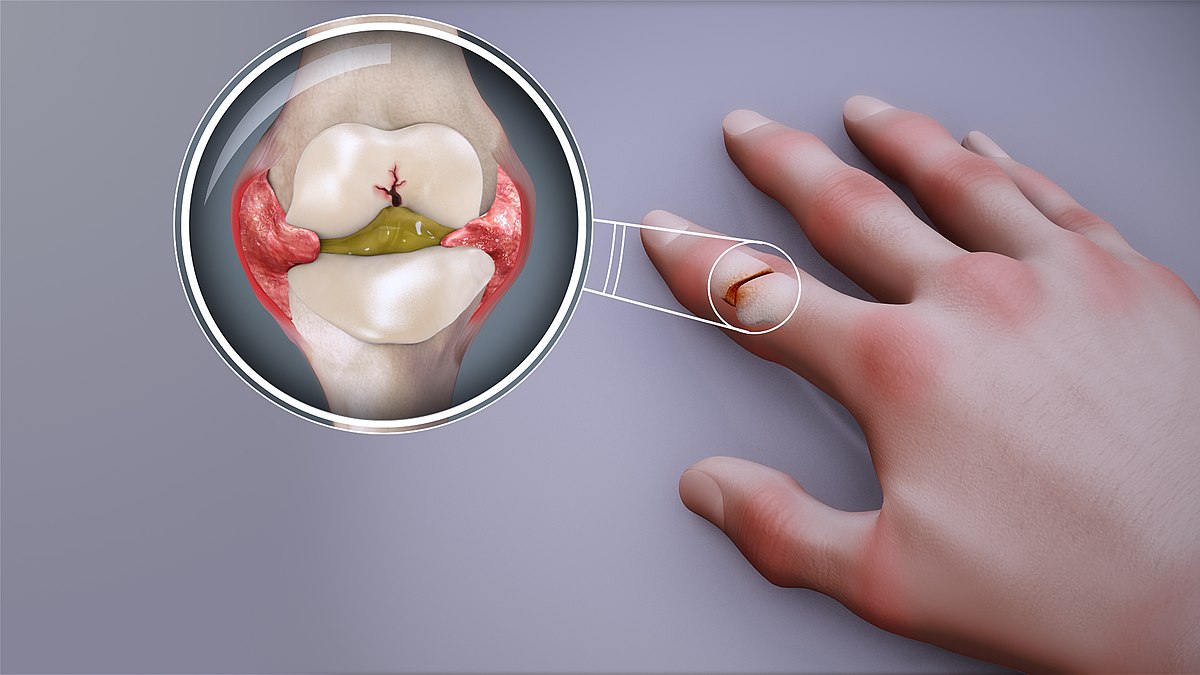
Rheumatism is a broad term that refers to various conditions causing chronic pain and inflammation in the joints, muscles, and connective tissues. It is often associated with autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. Some forms of rheumatism, like osteoarthritis, are due to wear and tear, while others result from an overactive immune system attacking the body’s own tissues.
Common Symptoms of Rheumatism
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling and redness in affected areas
- Fatigue and general discomfort
- Difficulty moving joints, especially in the morning
- Warmth around inflamed joints
Types of Rheumatic Diseases
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks joint linings, leading to inflammation and damage.
- Osteoarthritis (OA) – A degenerative joint disease caused by cartilage breakdown.
- Gout – A form of arthritis caused by uric acid crystal buildup in joints, leading to sudden and severe pain.
- Lupus – A systemic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs, including joints.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis – A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine and can lead to spinal fusion.
Treatment Options
- Medications: NSAIDs (like ibuprofen), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics.
- Physical Therapy: Helps maintain joint flexibility and strength.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and stress reduction.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and dietary supplements (such as omega-3 fatty acids).

