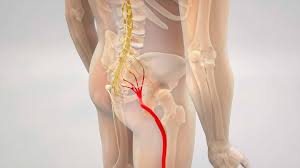
Sciatica
ChatGPT said:
Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down through the hips, buttocks, and legs. It is usually caused by compression or irritation of the nerve.
1. Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica is typically caused by conditions that put pressure on the sciatic nerve, including:
- Herniated or Bulging Disc – The most common cause, where a spinal disc compresses the nerve.
- Spinal Stenosis – Narrowing of the spinal canal that pinches the nerve.
- Piriformis Syndrome – Tightening or spasms of the piriformis muscle (in the buttocks) compressing the nerve.
- Spondylolisthesis – A slipped vertebra that presses on the sciatic nerve.
- Injury or Trauma – Accidents, falls, or sports injuries affecting the lower back.
2. Symptoms of Sciatica
- Radiating Pain – Starts in the lower back and moves down one leg.
- Numbness & Tingling – Often felt in the leg or foot.
- Muscle Weakness – In severe cases, can cause difficulty in movement.
- Worsening Pain with Movement – Symptoms may intensify with sitting, standing, or bending.
3. Treatment Options
A. Conservative Treatments (For Mild to Moderate Cases)
- Rest & Activity Modification – Avoid activities that trigger pain but stay moderately active.
- Cold & Heat Therapy – Ice packs reduce inflammation, while heat relaxes muscles.
- Pain Medications –
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) for pain and inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants (e.g., cyclobenzaprine) for muscle spasms.
- Neuropathic pain relievers (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) for nerve pain.
B. Physical Therapy & Exercises
- Stretching & Strengthening – To improve flexibility and reduce nerve compression.
- Posture & Core Strengthening – Helps maintain spinal stability.
- Manual Therapy – Chiropractors or physiotherapists may perform adjustments or massage therapy.
C. Advanced Medical Treatments
- Epidural Steroid Injections – Reduce inflammation around the nerve.
- Nerve Block Injections – Targeted pain relief for severe cases.
D. Surgical Intervention (For Severe or Chronic Sciatica)
Surgery is considered if symptoms persist for more than 6-12 weeks despite treatment or if there is significant nerve damage (e.g., weakness, bowel/bladder issues). Common procedures include:
- Microdiscectomy – Removes part of a herniated disc pressing on the nerve.
- Laminectomy – Removes part of the vertebra to relieve spinal stenosis pressure.
4. Prevention & Lifestyle Changes
- Maintain Good Posture – Avoid slouching and support the lower back when sitting.
- Regular Exercise – Strengthen core and back muscles to prevent recurrence.
- Lift Properly – Use legs instead of the back when lifting heavy objects.
- Weight Management – Reducing excess weight can lower spinal pressure

