Tinea Alba: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
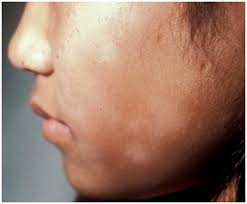
Tinea alba is a common, mild skin condition that appears as hypopigmented (light-colored) patches on the skin, mostly affecting children and adolescents. It is not a fungal infection despite its name (“Tinea”), but rather a form of mild eczema (atopic dermatitis).
Causes of Tinea Alba
- Unknown exact cause, but linked to dry skin and eczema.
- Common in children (ages 3-16 years).
- More noticeable in people with darker skin tones.
- Often worsens with sun exposure, harsh soaps, or dry weather.
Symptoms of Tinea Alba
- Pale or white patches on the face, arms, or upper body.
- Slight redness or scaling before turning pale.
- Mild itching or dryness (but often asymptomatic).
- Patches become more visible after sun exposure due to surrounding skin tanning.
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination by a doctor.
- Wood’s Lamp Test or KOH test to rule out fungal infections like tinea versicolor.
- Skin biopsy (rarely needed).
Treatment of Tinea Alba
1. Moisturization & Skin Care
- Use fragrance-free moisturizers (e.g., petroleum jelly, ceramide creams).
- Mild soap & lukewarm water (avoid harsh detergents).
2. Topical Medications (If Needed)
- Low-strength steroid creams (Hydrocortisone 1%) for inflammation.
- Pimecrolimus or tacrolimus creams (for persistent cases).
3. Sun Protection
- Use sunscreen (SPF 30+) to prevent contrast between normal and affected skin.
- Avoid excessive sun exposure.
4. Natural Remedies
- Aloe vera gel – Soothes dryness.
- Coconut oil – Helps retain moisture.
Is Tinea Alba Contagious?
No, it is NOT contagious.
How Long Does It Last?
- Usually fades within months but can last a few years.
- Often resolves completely by adulthood.
When to See a Doctor?
🔹 If patches persist or worsen despite treatment.
🔹 If severe itching or redness develops.
🔹 If unsure whether it’s Tinea Alba or a fungal infection (Tinea Versicolor, Vitiligo, or Pityriasis Alba).

